HTML & CSS Fundamentals
Introduction
Introduction to HTML5 & CSS3
HTML Basics
Introduction
HTML Elements
HTML Attributes
HTML Styles
HTML Formatting
HTML Tables
HTML Lists
HTML Forms
HTML Forms Attributes
CSS Basics
Introduction
CSS Selectors
CSS Integration
CSS Colors
CSS Backgrounds
CSS Borders
CSS Margins & Paddings
CSS Height & Width
CSS Box Modal
CSS Text
CSS Advanced
CSS Variables
CSS Media Queries
CSS Flexbox
CSS Flex Container
CSS Flex Items
CSS Grid
CSS Grid Container
CSS Grid Item
Introduction
CSS is the language we use to style a Web page.
What is CSS?
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
- CSS describes how HTML elements are to be displayed on screen, paper, or in other media
- CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once
- External stylesheets are stored in CSS files
Why Use CSS?
CSS is used to define styles for your web pages, including the design, layout and variations in display for different devices and screen sizes.
CSS Example
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color: white;
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-family: verdana;
font-size: 20px;
}CSS Solved a Big Problem
HTML was NEVER intended to contain tags for formatting a web page!
HTML was created to describe the content of a web page, like:
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
When tags like <font>, and color attributes were added to the HTML 3.2 specification, it started a nightmare for web developers. Development of large websites, where fonts and color information were added to every single page, became a long and expensive process.
To solve this problem, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) created CSS.
CSS removed the style formatting from the HTML page!
CSS Saves a Lot of Work!
The style definitions are normally saved in external .css files.
With an external stylesheet file, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file!
CSS Syntax
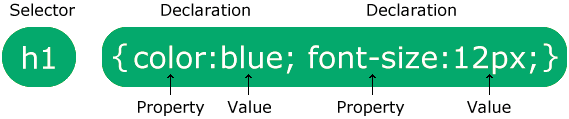
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
Multiple CSS declarations are separated with semicolons, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces.
Example
p {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}Example Explained
pis a selector in CSS (it points to the HTML element you want to style: <p>).coloris a property, andredis the property valuetext-alignis a property, andcenteris the property value
Note: You will learn much more about CSS selectors and CSS properties in the next chapters!